or call: +1 (845) 347-8894
or call: +1 (845) 347-8894
Big Data
Unlocking the Power of Information
Big data refers to massive and complex datasets that traditional data-handling methods struggle to manage and analyze efficiently.
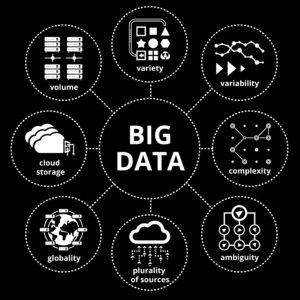
Big data is characterized by three key aspects, often referred to as the 3 Vs
Volume
This refers to the immense amount of data being generated and stored. Traditional data management tools often struggle with the sheer size of big data.
Velocity
This refers to the speed at which data is generated and processed. With big data, information comes in at an ever-increasing rate, requiring systems that can handle real-time or near-real-time processing.
Variety
This refers to the diversity of data types encountered in big data. It encompasses structured data (e.g., databases), semi-structured data (e.g., emails), and unstructured data (e.g., social media posts, and images), making it challenging to analyze and manage with traditional methods.
How is Big Data Used?
Big data is used in a wide range of applications across various industries
Healthcare
Analyzing patient data can help identify diseases, predict risks, and develop personalized treatment plans.
Finance
Big data is used to assess creditworthiness, detect fraud, and manage risk.
Retail
Analyzing customer data allows businesses to understand buying behavior, personalize marketing campaigns, and optimize product offerings.
Government
Big data is used to improve public services, manage resources efficiently, and combat crime.

Why is Big Data Important?
Big data holds immense potential for various sectors due to its ability to:
- Uncover hidden patterns and trends: By analyzing vast amounts of data, organizations can discover insights that wouldn’t be readily apparent with smaller datasets. This allows for informed decision-making and improved problem-solving across various fields.
- Enhance efficiency and productivity: Big data analytics can help optimize processes, identify areas for improvement, and automate tasks, ultimately leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Personalize experiences: Analyzing data allows companies to personalize experiences and offerings, catering to individual needs and preferences, which can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Drive innovation and advancements: Big data is being used in various fields to drive innovation and advancements. For example, it plays a role in developing new medical treatments, improving weather forecasting, and enhancing scientific research.
Big Data Management Technologies: Taming the Information Tsunami
The vastness and complexity of big data necessitate specialized technologies to manage, store, and analyze it effectively. Here’s an overview of some key big data management technologies:
- Distributed Processing Frameworks: These frameworks, like Apache Hadoop and Spark, enable parallel processing of large datasets across clusters of computers, allowing for faster and more efficient data processing.
- NoSQL Databases: Unlike traditional relational databases, NoSQL databases offer greater flexibility and scalability for handling diverse data types and structures commonly found in big data.
- Data Lakes: These central repositories store massive amounts of raw data in its original format, allowing for exploration and analysis later without the need for pre-defined schema.
- Data Warehouses: These are structured repositories designed for specific business needs, storing and organizing data for efficient analysis and reporting.
- Data Visualization Tools: These tools help translate complex data into easily understandable visual formats, like charts, graphs, and dashboards, facilitating data exploration and communication of insights.
The global Big Data market is projected to generate $103 billion in revenue by 2027 – SiliconANGLE, Wikibon
Big Data Challenges: Navigating the Information Maze
Data Storage and Management
Storing and managing massive amounts of data can be expensive and complex, requiring powerful hardware, specialized software, and skilled professionals.
Data Security and Privacy
Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse is crucial, requiring robust security measures and compliance with relevant regulations.
Data Quality and Integration
Ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and completeness is critical for reliable insights. Integrating data from various sources with different formats can be challenging.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Extracting meaningful insights from complex and diverse data sets requires advanced analytical skills, expertise in data mining techniques, and the ability to translate findings into actionable strategies.
Talent Shortage
The increasing demand for skilled data scientists, data engineers, and other big data professionals poses a challenge for many organizations.
Ethical Considerations
The use of big data raises ethical concerns, such as potential bias in algorithms, data privacy violations, and the implications of using personal data for decision-making.

The Human Touch in Big Data: Making the Most of Information
While big data promises valuable insights and a competitive edge, the success of these initiatives ultimately relies on the people who manage and analyze the information.
Q & A
Contact us
Just drop in a message for any queries. We would be more than happy to assist you.
