or call: +1 (845) 347-8894

or call: +1 (845) 347-8894
or call: +1 (845) 347-8894

In an age marked by swift strides in artificial intelligence (AI) technology, the pervasive adoption of AI systems signifies a transformative shift in managing vast datasets and navigating complex decision-making landscapes. The emergence of ChatGPT has underscored the formidable capacities of AI, casting a spotlight on its integration across diverse sectors. Notably, the realm of surveillance stands out, prompting crucial conversations about the equilibrium between security and privacy in the context of AI in surveillance and AI in spying. this confluence of technological innovation and ethical considerations reshapes the discourse surrounding the deployment of AI, especially in areas where surveillance intersects with the broader spectrum of AI applications.
AI surveillance represents a transformative shift away from conventional spying methods, which heavily rely on human efforts. This evolution is marked by an unparalleled expansion in both scope and efficiency. Traditional methods, including tapping phones and physical tracking, face limitations in the digital age, where individuals’ online activities contribute to an extensive and intricate digital footprint. In this era, governments and corporations leverage AI surveillance to monitor virtually every online move, giving rise to the creation of comprehensive profiles intricately linked to real-world identities.
The capabilities of AI increasingly overshadow the conventional approach to surveillance, with its manual and labor-intensive techniques. Unlike human-centric methods, AI surveillance thrives on automation, data analytics, and machine learning, enabling a more nuanced and sophisticated understanding of individuals’ behaviors, interactions, and preferences in the digital realm.
The applications of AI in surveillance encompass a wide array of possibilities, showcasing the extensive reach and transformative capabilities of artificial intelligence. The integration of AI extends beyond conventional methods, revolutionizing how we understand and implement surveillance technologies. This technological paradigm shift introduces nuanced applications that redefine the landscape of security and data management.
One significant facet of AI in surveillance lies in its ability to track online behavior comprehensively. The digital footprint left by individuals in the vast realm of the internet becomes a valuable source of data. AI systems excel in processing and analyzing this data, providing a holistic view of online activities. From monitoring social media interactions to analyzing browsing patterns, AI-driven surveillance ensures a meticulous understanding of individuals’ virtual presence.
Facial recognition emerges as a sophisticated application, leveraging advanced camera systems to identify and track individuals in various settings. Whether in public spaces, workplaces, or other environments, AI-enhanced facial recognition contributes to robust security measures. This technology transcends traditional surveillance methods, offering real-time identification and tracking capabilities, thereby enhancing situational awareness and response times.
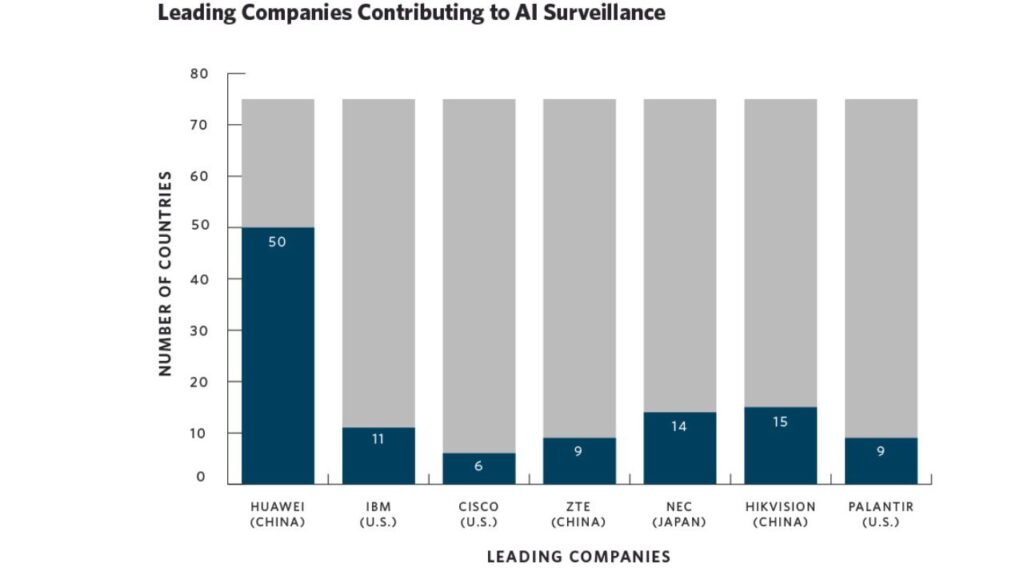
As AI technology advances, its role in automating surveillance becomes more pronounced. The sheer volume of digital data generated requires innovative approaches to data management.
– Data Collection: AI tools facilitate data collection from diverse sources, employing web scrapers with natural language processing capabilities to handle unstructured data effectively.
– Data Mapping and Quality Assurance: Data mapping and quality assurance also benefit from AI, as machine learning algorithms identify patterns and relationships, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
– Speech Analysis: AI excels in identifying individuals by voice, extracting keywords, and recognizing emotional states.
– Behavior tracking: It is the cream of the crop when it comes to surveillance and security. IA is now capable of tracking human behavior with a precision so accurate, that it will track your office time, and coming time and it will provide security measures according to that.
Beyond internet communications, AI-powered video surveillance systems profoundly enhance safety and monitoring capabilities in public spaces and urban environments.
– Facial Recognition: Facial recognition allows for the identification and tracking of individuals.
– License Plate Reading: Automatic license plate reading adds another layer to real-time tracking and It can be also used in self-driving technology.
– Retina/ Iris scan: This technology will enhance the facial registration system, adding security and making it more robust and reliable.
However, it’s crucial to emphasize that while AI plays a vital role in enhancing security through mass intelligence gathering, ethical considerations are paramount.
– Preventing Misuse: Ensuring accountability and preventing misuse are imperative aspects of deploying AI for surveillance purposes.
– Regulatory Frameworks: Striking a balance between security and privacy involves stringent regulations, transparency, and oversight to prevent unauthorized access or use of collected data.
Additionally, companies like Google and Meta, heavily reliant on user data for targeted advertising, introduce new challenges.
– Hyper-Precise Ads: The highly targeted ads from data analytics raise major concerns about user privacy and potential data misuse.
– Suggesting personalized Ads: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok have already shown a great interest in public data. It will give them great leverage to engage and interact with their existing audience.
To address these concerns, ethical guidelines and legal frameworks must be established to govern the use of AI in surveillance.
– Data Access Protocols: Strict protocols for data access and storage, as well as regular audits, can prevent misuse.
– Transparency from Tech Giants: Tech giants must communicate transparently about data practices to build trust and protect users’ rights.
The integration of AI into surveillance brings both advancements and ethical challenges. As technology evolves, it is crucial to prioritize accountability, transparency, and user privacy. AI can be a powerful tool for enhancing security, provided it is wielded responsibly and with a commitment to safeguarding individual rights. Balancing the benefits of AI surveillance with ethical considerations will shape the future of a secure and privacy-respecting digital landscape.
