or call: +1 (845) 347-8894

or call: +1 (845) 347-8894
or call: +1 (845) 347-8894

The vast expanse of a farm field might seem like a simple scene, but for farmers, it’s a meticulously managed ecosystem. Every decision – from seed selection to watering schedules – impacts crop yield and overall profitability. However, traditional farming methods can be labor-intensive, time-consuming, and even wasteful. This is where Agribots, specifically aerial drones, are revolutionizing the agricultural landscape.
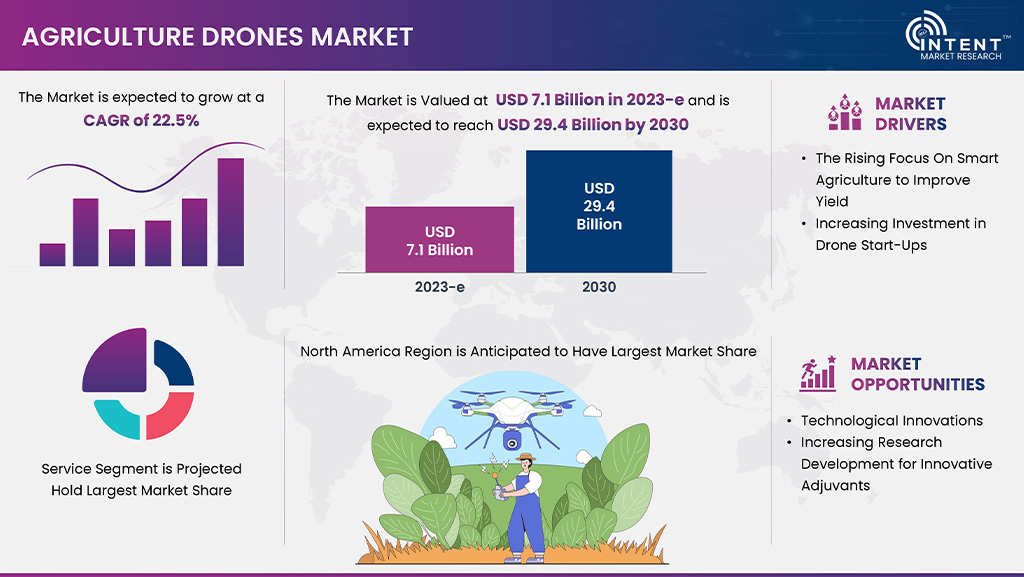
Also known as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), are no longer just toys or military tools. In agriculture, they’ve become versatile agribots, equipped for tasks like crop seeding and spraying. A 2023 Precision Agribusiness Market Report predicts the global precision agribusiness market, which includes drones, to reach a staggering $16.82 billion by 2025.
Drones are revolutionizing the way farmers scout and monitor plant health. These aerial platforms offer a unique vantage point and advanced sensors, allowing farmers to identify problems early and take targeted action. Here’s how drones are changing the game:
Unlike standard cameras, drones can be equipped with multispectral sensors that capture data beyond the visible spectrum. This allows farmers to detect subtle changes in plant health, like nutrient deficiencies or early signs of disease, before they become visible to the naked eye.
Drones can quickly cover vast fields, providing a comprehensive overview of crop health in a fraction of the time it takes for traditional ground scouting. Consequently, this allows for early detection of issues and quicker intervention.
Drones equipped with thermal imaging sensors can pinpoint areas with temperature variations, potentially indicating irrigation problems or stressed plants. This allows farmers to focus their scouting efforts on specific areas and optimize resource allocation.
Researchers use the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) with drone imagery as a popular tool. It measures the health and vigor of vegetation based on the reflectance of different wavelengths of light. Analyzing NDVI maps generated from drone data allows farmers to identify areas in the field that might require additional attention.
Source: Intent Market Research Analysis
Examples of how farmers are using drones for plant health monitoring:
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles can precisely plant seeds across vast fields, increasing efficiency and optimizing seed placement. A 2022 DroneDeploy case study highlights how a soybean farm in Illinois used Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for seeding, achieving a 98% planting accuracy rate compared to the industry average of 80-85% with traditional methods. This translates to significant cost savings and higher yields.
They can target specific areas of a field, minimizing herbicide and pesticide use by up to 70%. This targeted approach protects beneficial insects and reduces environmental impact. Imagine a drone precisely spraying fungicide on a small patch of diseased crops, instead of blanketing the entire field with chemicals.
California Startup, Augean Robotics, recently secured $16 million in funding to develop autonomous drones for high-speed, high-precision crop spraying.
John Deere, a major agricultural equipment manufacturer, acquired aerospace company Blue River Technology in 2017, a clear signal of their commitment to drone integration in farming.
Some additional benefits of using drones for plant health monitoring:
Drone technology in agriculture is still evolving, but the potential is undeniable. As battery life improves, flight ranges expand, and regulations adapt, drones promise to become even more sophisticated tools for farmers. The rise of Agribots signifies a future of smarter, more sustainable farming practices, leading to increased food production, reduced environmental impact, and a more efficient agricultural industry.
